Description
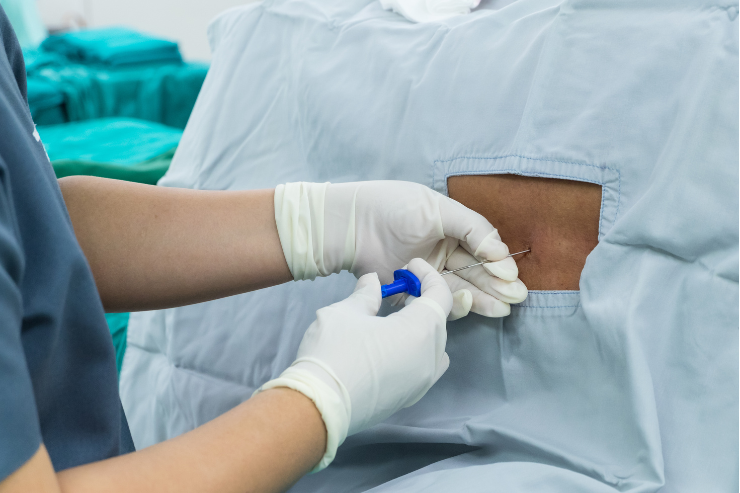
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are medical procedures used to examine the soft, spongy tissue inside bones, where blood cells are produced. These tests help diagnose blood disorders, cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma, and other bone marrow-related conditions.
How the Test is Done?
During bone marrow aspiration, a needle is inserted into the bone (usually the hipbone) to withdraw a small sample of the liquid portion of the marrow. For the biopsy, a thicker needle is used to remove a small core of solid bone marrow tissue. Both samples are sent to the lab for microscopic examination to assess cell production and health.
Preparation Required
Patients are typically advised to inform their doctor about any medications, especially blood thinners. Local anesthesia is usually applied, and the procedure may be done on an outpatient basis. In some cases, mild sedation may be offered. No fasting is usually required.
Significance of the Results
The results of a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy provide crucial information about the health of blood-forming cells, helping diagnose conditions like anemia, leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, and other marrow disorders. It also aids in monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for blood-related diseases.