Description
A urine test, also known as urinalysis, is a common diagnostic test used to evaluate various substances in the urine. It helps detect a wide range of conditions, including urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney disease, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders.
How the Test is Done?
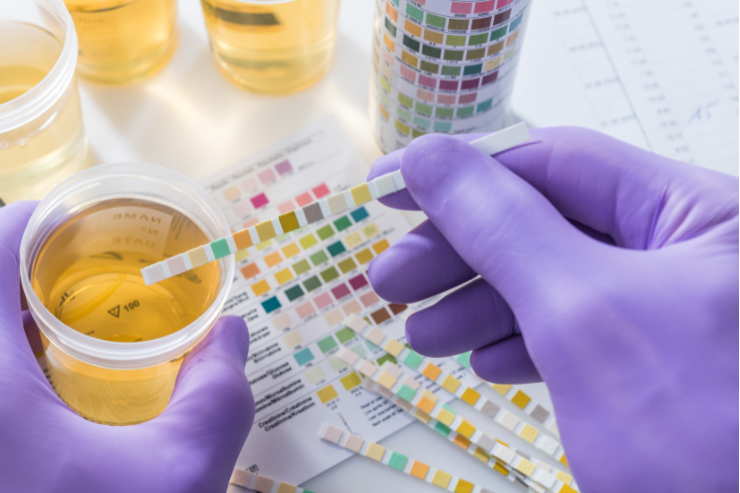
A urine sample is collected in a sterile container. The sample is then analyzed in a lab for its physical properties (color, clarity), chemical composition (pH, glucose, protein levels), and microscopic content (red and white blood cells, bacteria, crystals). Depending on the test, the urine may be tested immediately or cultured for bacteria.
Preparation Required
No special preparation is typically needed. However, it is advised to avoid heavy physical activity and certain foods or medications that could affect the test results. A “midstream” clean-catch urine sample is often recommended to prevent contamination from skin bacteria.
Significance of the Results
Urine test results can provide valuable information about hydration levels, kidney function, and the presence of infections, blood, sugar, or protein in the urine. Abnormal results can indicate conditions like UTIs, kidney disease, liver disease, diabetes, or pregnancy complications, and may prompt further testing or treatment.